Introduction
If you’re searching for how to convert 3.49e10 watts to GW, you’ve come to the right place. This guide will break down everything you need to know about this conversion in an easy-to-understand format. We’ll explore scientific notation, what 3.49e10 watts represents, and how it relates to gigawatts (GW). By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of power conversion from watts to gigawatts and how it’s used in the real world.
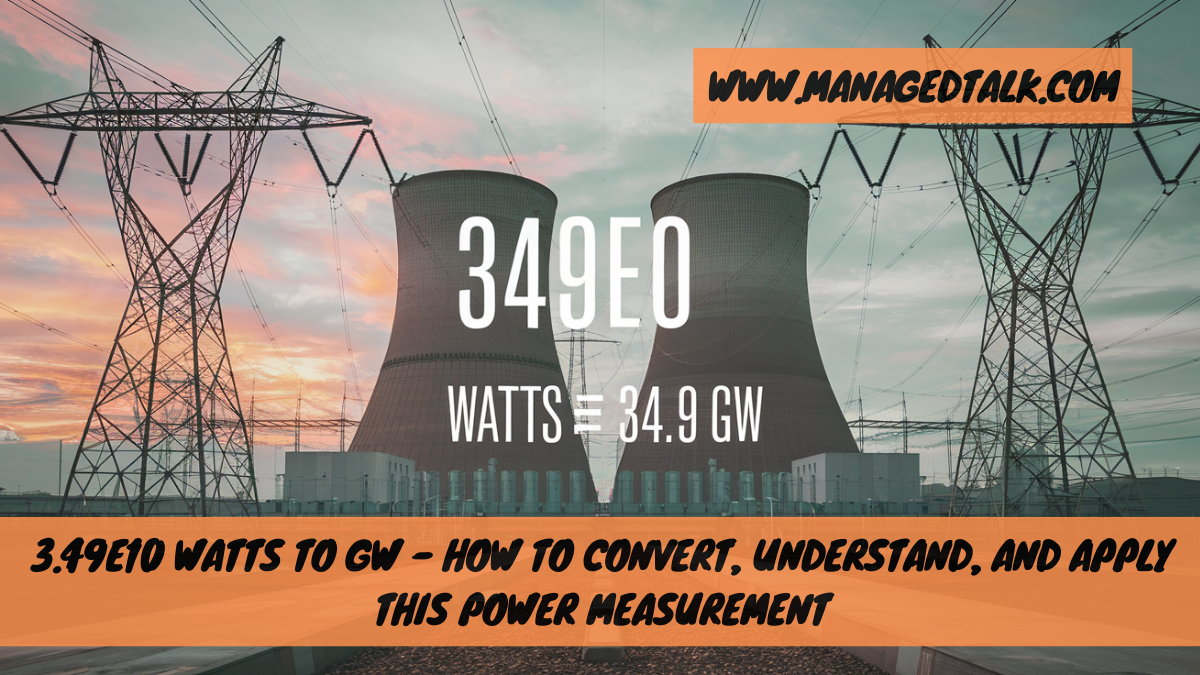
3.49e10 watts equals 34.9 gigawatts (GW). Gigawatts measure large-scale power generation, essential for industries and regions. This simple conversion helps in understanding vast energy outputs.
Whether you’re a student, engineer, or someone curious about energy and power, this guide is designed to make things as simple as possible. We’ll also include some real-life applications, practical examples, and frequently asked questions (FAQs).
What Does 3.49e10 Mean in Scientific Notation?
Before diving into the conversion, it’s essential to understand what 3.49e10 means.
Scientific Notation Explained:
The notation 3.49e10 stands for 3.49 × 10^10 watts. This is a compact way of representing very large or small numbers, which is often used in fields like physics, engineering, and energy production. The “e” represents the word “exponent,” meaning you multiply 3.49 by 10 raised to the power of 10. In simpler terms:
[ 3.49e10 \text{ watts} = 34,900,000,000 \text{ watts} ]
That’s quite a large number! Now, let’s convert this into gigawatts.
Converting 3.49e10 Watts to Gigawatts (GW)
Step-by-Step Conversion Process:
- 1 gigawatt (GW) is equal to 1 billion watts, or 1 GW = 1 × 10^9 watts.
To convert watts to gigawatts, you divide the number of watts by 1 billion:
[ \frac{3.49e10 \text{ watts}}{1 × 10^9} = 34.9 \text{ gigawatts (GW)} ]
So, 3.49e10 watts equals 34.9 gigawatts (GW).
Why Is This Important?
Gigawatts are commonly used when talking about large-scale power generation, such as the output of power plants or the energy consumption of entire cities. Converting watts to gigawatts is useful when discussing or calculating high levels of energy production or consumption.
For example, a nuclear power plant may generate between 1 to 1.5 gigawatts of electrical power. This means that 3.49e10 watts, or 34.9 gigawatts, is equivalent to the output of about 35 large power plants!
Real-Life Applications of Gigawatts
Understanding the scale of gigawatts helps when comparing energy usage or generation across different sectors:
- Power Plants: Most large power plants generate between 1 to 3 GW of energy. Converting 3.49e10 watts to gigawatts helps put into perspective how much power an entire region or country consumes.
- Renewable Energy: Wind farms and solar power plants also measure their output in gigawatts. For instance, a large wind farm may generate around 1 GW of power, which can supply electricity to around 700,000 homes.
- Data Centers: Massive data centers that store and process internet data require gigawatt levels of power to keep everything running efficiently.
How Does This Compare to Other Power Units?
To put gigawatts in context, here are some comparisons:
- 1 kilowatt (kW) = 1,000 watts
- 1 megawatt (MW) = 1,000,000 watts (or 1 × 10^6 watts)
- 1 gigawatt (GW) = 1,000,000,000 watts (or 1 × 10^9 watts)
By converting 3.49e10 watts to GW, you can see that the number is significant in large-scale power generation.
Understanding Power and Energy
It’s important to note that power (measured in watts or gigawatts) is different from energy (measured in watt-hours or gigawatt-hours). Power refers to the rate at which energy is produced or consumed, while energy refers to the total amount produced or consumed over time.
For example, if a power plant generates 1 gigawatt of power continuously for an hour, it produces 1 gigawatt-hour (GWh) of energy. Therefore, if 34.9 gigawatts of power were used for one hour, it would generate 34.9 GWh of energy.
How Is This Conversion Used in the Real World?
Converting watts to gigawatts is commonly used in industries like:
- Energy Production: Power plants, especially nuclear and renewable energy plants, often measure their output in gigawatts.
- Electrical Grid Management: Operators of electrical grids use gigawatt measurements to balance supply and demand for entire regions.
- Large-Scale Energy Consumers: Industries such as manufacturing or data centers often consume power on the gigawatt scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is 3.49e10 watts in gigawatts?
3.49e10 watts is equal to 34.9 gigawatts (GW).
2. Why do we use scientific notation like 3.49e10?
Scientific notation simplifies the representation of very large or very small numbers, making it easier to read and work with in calculations.
3. What is a gigawatt (GW)?
A gigawatt is a unit of power equal to 1 billion watts. It is commonly used to measure the output of power plants or the electricity usage of large populations.
4. How is the conversion from watts to gigawatts done?
To convert watts to gigawatts, divide the number of watts by 1 billion (1 × 10^9). For example, 3.49e10 watts ÷ 1 × 10^9 = 34.9 gigawatts.
5. What is the practical application of gigawatts?
Gigawatts are used to measure large-scale power generation, such as the output of nuclear power plants or the capacity of large renewable energy installations like wind farms.
Conclusion
Converting 3.49e10 watts to GW is simple once you understand the relationship between watts and gigawatts. 3.49e10 watts is equal to 34.9 gigawatts, a measurement often used in industries like power generation, grid management, and large-scale energy consumption. This conversion is particularly important for understanding how much power is needed to support cities, industries, and renewable energy efforts. Understanding these concepts empowers you to better comprehend large-scale energy discussions and make informed decisions about energy use and efficiency.